Explore the Mechanism of Action

IFN-ɣ driven Inflammation in Vitiligo is JAK-mediated⁴
IFN-γ mediated JAK-STAT signaling is thought to drive an inflammatory cycle, creating a hostile environment in which CD8+ T-cells target and destroy melanocytes.⁴ Autoimmune IFN-γ producing cytotoxic T lymphocytes are thought to be directly responsible for melanocyte destruction in human vitiligo.⁵

Adapted from ref. 4
The Role of the JAK-STAT Pathway in Vitiligo⁴
Intrinsic and/or extrinsic factors induce the cellular stress response in melanocytes, which then
activates innate immunity within the skin to trigger the initial inflammation that leads to
autoimmunity.⁴
1- CXCL9 and CXCL10 are released from keratinocytes, leading to the recruitment of CD8+ T cells.⁴
2- Activated CD8+T cells produce IFN-γ, which triggers more CXCL9 and CXCL10 production from
keratinocytes through JAK1 and JAK2 signaling and recruits more CD8+ T cells to the inflamed sites.⁴
3- CD8+ T cells then destroy melanocytes and lead to depigmentation.⁴
Lumirix® (ruxolitinib 15mg/g) cream is a Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor.³
Ruxolitinib cream has been found to have physicochemical properties suitable for topical delivery through the skin of patients with inflammatory skin diseases.6
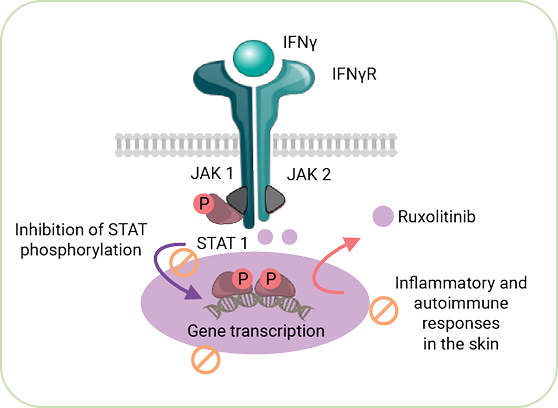
Adapted from ref. 7
Lumirix® (ruxolitinib 15mg/g) cream can be a promising treatment for vitiligo.⁸
In addition to Ruxolitinib's anti-IFN-γ effect, it also seems to activate the hair follicle melanocyte stem cell.⁸
IFN-ɣ: Interferon gamma; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription; CD: Cluster of Differentiation.
References:
- 3. Lumirix® Prescribing Information for Hong Kong.
- 4. Howell MD, Kuo FI, Smith PA. Targeting the Janus kinase family in autoimmune skin diseases. Front Immunol. 2019; 10: 2342 [Internet]. 2019.
- 5. Frisoli ML, Essien K, Harris JE. Vitiligo: mechanisms of pathogenesis and treatment. Annual review of immunology. 2020;38(1):621-48.
- 6. Smith P, Yao W, Shepard S, Covington M, Lee J, Lofland J, Naim A, Sheth T, Parikh B, Yeleswaram S. Developing a JAK inhibitor for targeted local delivery: ruxolitinib cream. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(7):1044.
- 7. Utama A, Wijesinghe R, Thng S. Janus kinase inhibitors and the changing landscape of vitiligo management: a scoping review. International Journal of Dermatology. 2024 Apr 12.
- 8. Birlea SA, Goldstein NB, Norris DA. Repigmentation through melanocyte regeneration in vitiligo. Dermatologic clinics. 2017 Apr 1;35(2):205-18.